Deep Reinforcement Learning for Optimizing Traffic Light Signals
Embedded in the research project KIVI (Künstliche Intelligenz im Verkehrssystem Ingolstadt; engl.: Artificial Intelligence in the Ingolstadt Traffic System), we are working on a doctoral project on the optimization of traffic signal systems using reinforcement learning.
Project description
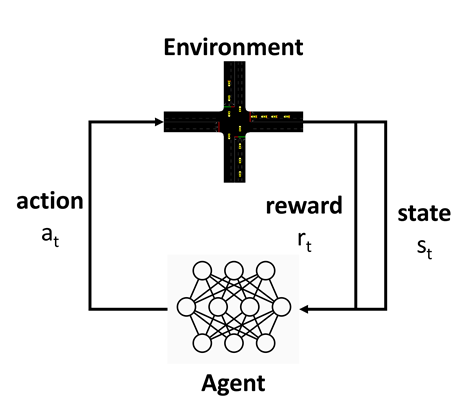
Efficient traffic systems are becoming increasingly important for reducing travel times and emissions. Intelligent traffic light systems play a key role here. Ideally, they guide traffic with the shortest possible travel time for all road users and minimal emissions, even with different traffic loads and requirements. Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) methods are a promising way of meeting these requirements. Here, an agent learns to maximize a reward by interacting with the environment, with neural networks serving as function approximators within the agent. In the context of traffic lights, the agent is given information about the current traffic situation, decides how to switch the traffic lights and then receives feedback from the environment on how the decision has affected the travel time and emissions of road users. In addition to the general evaluation of DRL for the optimization of traffic light systems and the selection of the best DRL setup, the following further questions are considered in the doctoral project:
- How can the distribution of green times be implemented fairly in a multimodal traffic volume?
- How can the "black-box" problem of DRL be overcome in the context of traffic signal optimization?
- How can Car2X functionalities be integrated in the optimization problem?
In the research project Künstliche Intelligenz im Verkehrssystem Ingolstadt (KIVI, engl.: Artificial Intelligence in the Ingolstadt Traffic System), data-driven artificial intelligence methods for traffic control and road safety in Ingolstadt are being developed together with project partners such as the Technical University of Munich, Fraunhofer IVI, GEVAS software GmbH and CARIAD SE. Among other things, a High Definition Test Area (HDT) consisting of three highly frequented traffic junctions will be equipped with local sensors to detect road users and use the information for the AI algorithms. The traffic junctions in the HDT are therefore ideal for testing the developed DRL algorithms for optimizing traffic signal systems in reality.




![[Translate to English:] Logo Akkreditierungsrat: Systemakkreditiert](/fileadmin/_processed_/2/8/csm_AR-Siegel_Systemakkreditierung_bc4ea3377d.webp)








![[Translate to English:] Logo IHK Ausbildungsbetrieb 2023](/fileadmin/_processed_/6/0/csm_IHK_Ausbildungsbetrieb_digital_2023_6850f47537.webp)


